용어 정리
1. POJO
- Plain Old Java Object
- 플랫폼에 독립적인 형태의 클래스를 의미한다.
예> CartListServlet는 의존적인 클래스( extends HttpServlet 때문에 Tomcat이 설치된 웹개발에서만 사용가능)
==> 서블릿은 extends HttpServlet이라는 API가 필요하고 실제 서비스되는 압축파일은 servlet-api.jar
servlet-api.jar를 얻을려면 Tomcat을 설치해야함
===> 서블릿은 의존적
예> DTO
==> DTO는 SE에서도 쓸 수 있고 어떤 환경에서도 쓸 수 있다
==> 독립적
2. (Spring) Bean
- Spring 환경에서 사용되는 POJO 기반의 클래스 의미.
- 개발자가 직접 Bean(클래스)을 new 하지 않음.
Bean을 자동으로 관리하는 또 다른 Bean(IoC Container)이 제공됨.
서블릿의 생성과 소멸을 관리하는 것은 톰캣
스프링을 관리하는 건 컨테이너(빈) , 빈이 빈을 관리한다, 클래스가 클래스를 관리
설치하거나하는게 아니라서 가벼워서 많이 씀
컨테이너는 IoC 컨테이너
서블릿이 서비스와 DAO 연결을 해줬지만
스프링은 IoC컨테이너가 한다
스프링 특징
1. 개발자가 Bean(클래스)을 new 하지 않는다
2. IoC컨테이너가 new를 하는데 컨테이너 자체도 Bean이다 ( 클래스가 클래스를 관리한다)
3. IoC 컨테이너
Core Technologies
In the preceding scenario, using @Autowired works well and provides the desired modularity, but determining exactly where the autowired bean definitions are declared is still somewhat ambiguous. For example, as a developer looking at ServiceConfig, how do
docs.spring.io
- 개념:
IoC(Inversion of Control) 방법으로 Spring Bean을 관리(생성~소멸)하기 때문에 붙여진 이름
- 비슷한용어:
Spring Container
Spring Context
- 기능:
Spring Bean을 관리(생성~소멸) 및 의존성 설정(DI:Dependency Injection: 의존성 주입).
(이전 개발방식은 클래스를 직접 생성하고 의존성도 직접 설정했음.
이런 순방향의 개발이 아닌 완전히 역방향의 개발이기 때문임.
)
- IoC Container의 실체는 Spring Bean이다. 계층구조로 되어 있음.
BeanFactory ( 인터페이스 )
| |
XXXApplicationContext XXXBeanFactory
|
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
GenericXmlApplicationContext
XXXWebApplicationContext ( web이 있는 것은 웹어플리케이션 개발용 IoC Container 임)
BeanFactory: 기본 Spring Container 임.
ApplicationContext : 기본기능 + enterprise 환경에서 필요한 전용기능이 추가된 컨테이너임
( 웹개발가능. I18N(국제화:InternationalizatioN), AOP 기능,.. )
의존성 ex>
장바구니 목록
CartService
웹브라우저 ----> CartListServlet ("/cartList") --> CartServiceImpl -------> CartDAO
| 요청위임(forward/redirect)
<---------- cartList.jsp
public class CartServiceImpl implments CartService{
CartDAO cartDAO;
public CartServiceImpl(CartDAO cartDAO){
this.cartDAO cartDAO'
}
# CartListServlet
CartService service = new CartServiceImpl(new CartDAO());
==> CartServiceImpl 와 CartDAO 간에 의존성이 생겼고
개발자가 명시적으로 CartServiceImpl에 CartDAO를 생성해서 값을 전달해줌.
프로젝트의 순서대로 서블릿이 서비스에, 서비스가 DAO에 의존성이 있다
중요 - 클래스들은 우리가 생성하고 의존성도 우리가 설정한다
서블릿에서는 의존성을 우리가 설정해줬다
스프링부트는 IoC 컨테이너가 new를 해준다
4. DI(Dependency Injection: 의존성 주입)
- 의존성? A 클래스가 B를 사용하면 A와 B간에 의존성이 생김.
- 의존성 주입? A(CartService)클래스가 B(CartDAO) 를 참조하기 위해서 외부(CartListServlet)에서
A 클래스의 생성자에 B 객체를 생성해서 설정하는 작업을 의미.
* Spring에서는 외부 역할(서블릿)을 IoC Container가 담당한다.
- 의존성 주입 방법
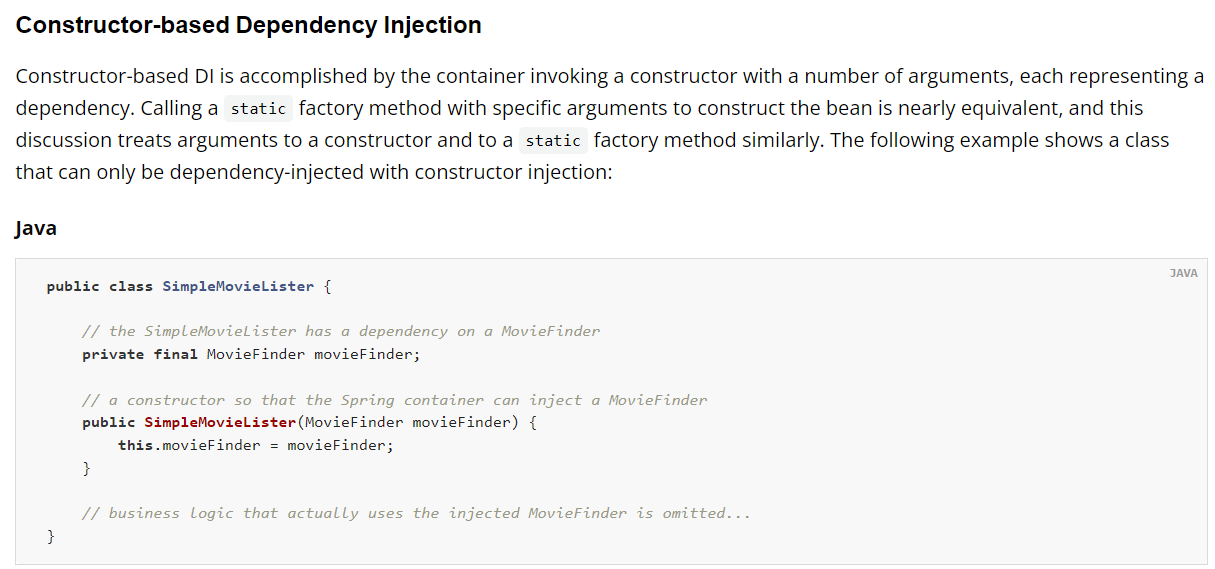
가. 생성자 이용한 주입
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.2.25.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#beans-constructor-injection
Core Technologies
In the preceding scenario, using @Autowired works well and provides the desired modularity, but determining exactly where the autowired bean definitions are declared is still somewhat ambiguous. For example, as a developer looking at ServiceConfig, how do
docs.spring.io
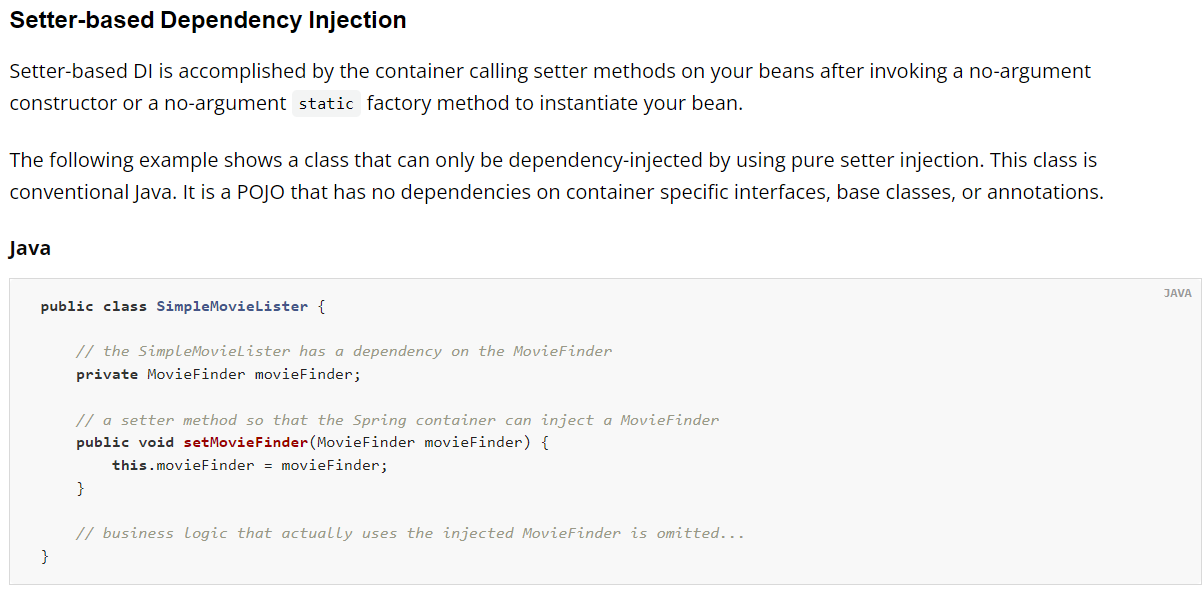
나. set메서드 이용한 주입
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.2.25.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#beans-setter-injection
Core Technologies
In the preceding scenario, using @Autowired works well and provides the desired modularity, but determining exactly where the autowired bean definitions are declared is still somewhat ambiguous. For example, as a developer looking at ServiceConfig, how do
docs.spring.io
'Spring Boot (Maven)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스프링부트 백그라운드5 ( 로깅처리 ) (0) | 2024.06.08 |
|---|---|
| 스프링부트 백그라운드4 ( 스프링부트 장점, 특징 ) (1) | 2024.06.08 |
| IoC Container에게 Bean(클래스)정보 같은 데이터를 알려주는 방법 ( Configuration 작업 ) (0) | 2024.06.03 |
| 스프링부트 백그라운드3 ( 빌드툴 ) (0) | 2024.06.02 |
| 스프링부트 백그라운드(설치) 1 (0) | 2024.06.01 |